SSDs are becoming more and more advanced and now offer as much storage space as a hard disk. With the emergence of the new M.2 format, the SSD can boot an operating system in only 10 seconds. Similarly, software and data transfers run almost instantaneously. But which M.2 SSD to choose? To find out, check out our guide to the best M.2 SSDs of the moment.
Here is our commitment, to make sure that we provide the best user experience and content quality:
You can support us by using our links to make your purchases (at no extra cost to you)! This sometimes earns us a commission which allows us to remain independent. More about us
Our selection
"Put an M.2 SSD at the heart of your PC for responsive, optimized performance. The WD Blue SN550 NVME drive is fast for working, creating,…"
"The Crucial P5 CT500P5SSD8 500GB features a state-of-the-art PCI.e 3.0 3D NAND controller. In theory, this M.2 SSD can achieve sequential read speeds of 3.4GB/s…"
"The WD Black SN750 2Tb is a very fast NVMe M.2 SSD. It has a heat sink, which cools the storage module. Count up to…"
"The Sabrent Rocket NVMe PCIe 4.0 M.2 2280 2TB internal SSD delivers extreme performance. It's backward compatible with PCIe 3.0 and offers all the benefits…"

Put an M.2 SSD at the heart of your PC for responsive, optimized performance. The WD Blue SN550 NVME drive is fast for working, creating, playing, or processing large amounts of data.
See priceThe WD Blue SN550 NVMe SSD is a reliable 1TB NVMe storage solution in M.2 2280 form factor. The storage drive uses a PCI Express 3.0 connector with a very low power consumption of 3.5W. The 3D NAND flash memory is a 3-bit multi-layer TLC 96 design, some of which is a 1-bit SLC cache.
Note that performance varies depending on the software installed as well as the hardware configuration of your PC. This M.2 SSD offers a sequential read speed of up to 2.4 GB/s, which is very useful for copying or downloading large files.

The Crucial P5 CT500P5SSD8 500GB features a state-of-the-art PCI.e 3.0 3D NAND controller. In theory, this M.2 SSD can achieve sequential read speeds of 3.4GB/s and sequential write speeds of 3GB/s.
54,50 £ on DartyNo matter what you do, the P5 SSD offers great performance. Designed with NVMe PCIe Gen3x4 technology, the Crucial P5 CT500P5SSD8 has advanced features like dynamic write acceleration and full hardware encryption. The storage medium features ECC and adaptive thermal protection to protect your data while maintaining high transfer speeds.
The Crucial P5 CT500P5SSD8 has a capacity of 500GB and uses 3D NAND technology, as well as an advanced controller. It can reach 3400 MB/s reading and 3000 MB/s writing. In this sense, it can outperform third-generation PCI express NVMe. Moreover, it remains mechanically compatible with both NVMe and AHCI hybrid M.2 system.

The WD Black SN750 2Tb is a very fast NVMe M.2 SSD. It has a heat sink, which cools the storage module. Count up to 3470 MB/s reading and 3000 MB/s writing, enough to suit the most demanding.
See priceThe WD Black SN750 is an SSD in M.2-2280 format, capable of operating a PCI-Express 3.0 x4 interface with support for the NVMe 1.3 protocol. This SSD is mostly dedicated to gamers, professionals. It has a heat sink, which allows it to run for a long time without losing performance. The WD Black SN750 has a transfer rate of 3.4 GB/s read and 2.9 GB/s write. This equates to 4 sec to transfer 10 GB of data.
The WD Black SN750 NVMe SSD offers 2GB of capacity and 64-layer 3D TLC NAND flash memory. For an additional 450 euros, you could afford the 4TB version, which is just as fast, but with twice the storage!

The Sabrent Rocket NVMe PCIe 4.0 M.2 2280 2TB internal SSD delivers extreme performance. It's backward compatible with PCIe 3.0 and offers all the benefits of the PCIe Gen 4.0 x4 interface. It is suitable for leisure and work.
See priceThe Sabrent Rocket Nvme PCIe 4.0 M.2 2280 SSD offers 2TB of storage. It offers all the benefits of flash drive technology with the fourth generation PCI express interface. Based on Toshiba's BiCS4 96L TLC NAND flash memory, its speeds reach 5,000 MB/s read and 4,400 MB/ s write on a PCIe Gen4 motherboard. But on a PCIe Gen3 motherboard, the speeds will be limited to 3400 MB/s read and 2750 MB/s write.
This SSD has an aluminum structure that is compatible with flash drives with the next-generation standard NGFF interface. The power consumption is much lower than that of traditional hard drives. This type of SSD supports bad block and over-provisioning management with SMART and TRIM commands as well as ONFi 2.3, ONFi 3.0, ONFi 3.2 and ONFi 4.0 interfaces.
Any specific needs?
Your guide :
Rate this buying guide :By rating this buying guide, you are helping us to reward our best writers. Thank you!
| TOP OF THE TOP | CHEAP | TOP OF THE LINE | EXCELLENT | |

In accordance with our commitment, this buying guide does not contain any sponsored products. |
 9/10 |
 8/10 |
 8/10 |
 7/10 |
| OUR SELECTION |
WD Bleu SN550 1 To
|
Crucial P5 CT500P5SSD8 500 Go
|
WD Black SN750 NVMe 2 To avec dissipateur
|
Sabrent M.2 2280 Rocket Nvme PCIe 4.0 de 2 TB avec dissipateur
|
|
Put an M.2 SSD at the heart of your PC for responsive, optimized performance. The WD Blue SN550 NVME drive is fast for working, creating, playing, or processing large amounts of data.
|
The Crucial P5 CT500P5SSD8 500GB features a state-of-the-art PCI.e 3.0 3D NAND controller. In theory, this M.2 SSD can achieve sequential read speeds of 3.4GB/s and sequential write speeds of 3GB/s.
|
The WD Black SN750 2Tb is a very fast NVMe M.2 SSD. It has a heat sink, which cools the storage module. Count up to 3470 MB/s reading and 3000 MB/s writing, enough to suit the most demanding.
|
The Sabrent Rocket NVMe PCIe 4.0 M.2 2280 2TB internal SSD delivers extreme performance. It's backward compatible with PCIe 3.0 and offers all the benefits of the PCIe Gen 4.0 x4 interface. It is suitable for leisure and work.
|
|
|
Capacity
|
1 TB
|
500 GB
|
2 TB
|
2 TB
|
|
Flash NAND
|
3D TLC
|
TLC
|
++++
|
TLC
|
|
Read and write speed
|
2,400 MB/s1,950 MB/s
|
3,400 MB/s3,000 MB/s
|
3 400 MB/s2 900 MB/s
|
5,000 MB/s4,400 MB/s
|
|
Lifetime
|
1,700,000 h
|
1,800,000 h
|
1 750 000 h
|
1,700,000 h
|
|
Dimension
|
8 x 2.2 x 0.24 cm
|
7.98 x 0.2 x 2.18 cm
|
8 x 2.4 x 0.8 cm
|
8 x 2.18 x 0.28 cm
|
Help us improve this table:
Report an error, request the addition of a feature to the table, or suggest another product. Thank you for your kindness!
We spend thousands of hours each year studying the major specialized websites, analyzing products of hundreds of brands and reading user feedback to advise you on the best products.
We are a product review company with a single mission: to simplify your buying decisions. Our research and testing helps millions of people every year find the best products for their personal needs and budget.
To support us you can: use our links to make your purchases (which often earns us a small commission), share our articles on social networks, or recommend our site on your blog. Thanks in advance for your support!
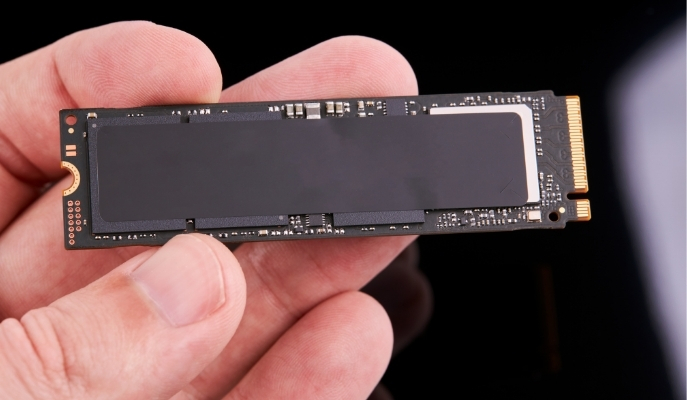
When you decide to change or upgrade your PC with an M.2 SSD, choose a good size that is suitable and available. Mostly expressed in millimeters, this is to make sure that the width and length will fit into the available space on your computer's motherboard. This is mainly an issue with laptops. Most SSDs will have a width of 22mm. While the length will vary. The most common length diverges between 42 mm, 60 mm, 80 mm and 110 mm.
The SSDs in M.2 format are compatible with the vast majority of motherboards. Regarding the interface, between SATA, PCI-express and NVMe, one can quickly get lost and must pay attention to the compatibility of the motherboard. SATA, the oldest, offers the same performance as traditional SSDs. The PCI-express allows to have performances about three times higher than the SATA interface. And finally NVMe offers an extremely wide range of performance, from entry-level to the highest-performance SSDs.
SSDs differ in the type of flash memory. A flash memory cell stores 1 to 4 bits of data depending on the technology. In theory, the higher the number of bits, the lower the memory performance, especially for writing, with a shorter lifespan. There are four types of NAND Flash:
Read and write speeds will be what most users consider. This speed will mostly define the performance of the SSD module and will be measured in megabytes per second reading and writing data. This will take care of the speed of running applications and booting your computer. For most SSD performance improvements, a faster read speed is much more critical than a faster write speed. But just as an FYI, most of the numbers listed are theoretical guidelines provided by the manufacturers.
Any flash memory has a limited lifetime, which means that once a given storage cell is written a certain number of times, it will stop holding data. Mean TimeBetween Failure or MTBF measured in thousands of hours is a measure of reliability that is used with varying definitions in various industries. Disk manufacturers often specify a disk's rated endurance in total terabytes written (TBW) or disk writes per day (DWPD). But most disks have over-provisioning, which reduces a portion of the disk's capacity into a kind of backup.
When buying an M.2 SSD, the first thing to know is whether your motherboard is compatible with it. M.2 is just the stick form factor of the SSD, but the more important detail is that there are slower M.2 SATA drives and faster M.2 NVMe drives, which use different keys. Even if your motherboard has an M.2 slot, its compatibility with your new M.2 drive will depend on whether the slot is compatible with B Key, M + B Key or M Key drives.
The location of the M.2 SSD on your PC's motherboard varies by manufacturer and board model. The most common places to find an M.2 slot are between the GPU and the CPU, or in the lower right-hand corner of your motherboard. Some motherboards even have a special metal plate that covers the M.2 drive, try unscrewing it first. Once you have removed all the obstructing hardware, it is time to insert your M.2 drive into the M.2 slot.
After these steps, engage your installation by unscrewing the mounting screw near the M.2 slot. If your M.2 player came with brackets, you should screw them in now. This will ensure that when you screw the drive in, it will be parallel to the motherboard, rather than angled towards it. Then carefully insert your M.2 drive into the M.2 slot at a 30 degree angle to the motherboard.
Gently press the upward slanted end of the drive towards the screw mount, then secure it with the mounting screw. Reinsert all the hardware and components you had to remove earlier, close your PC case.
To complete your installation, you may need to configure some things in the BIOS of your motherboard. The changes you need to make will depend on your motherboard's capabilities. To access them, open your BIOS. The exact process from here will vary depending on your motherboard.
Flash memory array manufacturing processes play a key role in cell endurance, which decreases as arrays become smaller. M.2 SSD Flash NAND devices can use MLC, TLC or SLC structures. MLC is the most common while TLC is the cheapest.
MLC or Multi Level Cell memory allows two bits of data to be stored on one cell. There are therefore four different possible values: 00, 11, 01, and 1. In fact, the MLC makes it possible to extend the storage capacity without increasing the size of the SSD with 3000 to 5000 possible write cycles per cell. On the other hand, the writing speed is slower and less precise.
This is currently the most commonly used type of SSD as it is mainly used in office or family computers. This type of SSD M.2 is especially recommended for gamers and amateurs who use the computer very often.

The
SSD TLC or Triple-level cell allows each cell to keep three pieces of data. Thus, its storage capacity is higher for a much cheaper price. On the other hand, the writing and reading speed is slower and less accurate hence the power consumption is even higher than MLC SSD. By storing 3 bits of data per cell, its lifetime is 500 to 1000 cycles per cell.
Admittedly, the lifespan is much shorter as well as the read and write speed is slower compared to SLC and MLC. It is mostly designed for daily use of users. The major problem with M.2 SSDs with this type of memory is that their guaranteed write cycles are about 3 to 5 times lower than MLC memory, which is worth about at 1,000 cycles per cell.
SLC or Single Level Cell is the fastest with a lifetime of up to 50,000 cycles per cell. However, it is also the most expensive and only concerns the lowest storage capacities by its ability to hold 1 bit per cell. Each cell can only read two different values. SSDs with this type of memory are intended for servers.
SLC memory is more accurate when reading and writing data. It can operate in a wide temperature range. And there are few read and write errors. This type of M.2 SSD is intended for industrial use requiring massive read and write cycles.
The M.2 SSDs are compatible with the NVMe protocol, which allows you to take advantage of a great read transfer rate of over 2500 MB/sec. However, it is important to take into account that the motherboard is equipped with this connection. The throughput can be as high as 10,000 MB/s.
Currently, all the most powerful motherboards on the market are equipped with this format. M.2 offers the possibility of using various types of SATA socket cards. M.2 cards are available in different lengths and widths. Its advantage is the possibility to combine M.2 SSDs with mechanical HDDs and 2.5 SSDs to save your data.
Its drawback is that if you plan to assemble your PC, we advise you to go for a motherboard with an M.2 port. Check the specifications of your equipment to see if it has such a port.
This is the "classic" format. It is also the most popular. It is the same format as mechanical hard drives. The 2.5 format is reserved for portable PCs. It is a format similar to the old mechanical drives. Except for M.2 which offers a higher throughput, all other formats offer a similar throughput for a more affordable cost.
Note that if you have a laptop, you will have to choose between keeping your old hard drive or switching to an SDD. If you choose the latter, look for a large-capacity SSD so you can put a lot of data on it.
Your choice will be guided by your motherboard's capability and your budget. The M.2 format guarantees a very high performance but with very limited motherboard connections. On the other hand, the 2.5 format remains a classic and the most popular model, but with less performance.
Extend the life of your M.2 SSD
The software supplied with your SSD allows you to activate TRIM in your operating system. This option optimizes data deletion. The OS informs the SSD about the blocks of data that are no longer used after a file deletion. This allows the drive to operate more efficiently, reduces the effect of write amplification and ultimately leads to faster performance and longer life. Adopting Over Provisioning is to reserve a portion of the SSD's disk space. This allows the SSD to be optimized. Indeed, the SSD controller can use this disk space to store temporary data. But above all, it will use the cells for Bad-Block-Management. So this allows to reduce the lifetime.
Know what type of storage your PC has
Two
methods are given to know your storage type: in Powershell, there are commands that allow you to get information including information about the hard drives. To launch PowerShell: on Windows 10, open the start menu then Windows PowerShell. On Windows 7, go to the Start menu > Accessories > Windows Powershell then enter the command to get an informative table about your hard drives, including the MediaType column indicates the format of your drive.
Measuring the speed of your M.2 SSD
Depending on
the spin speed and cache, the measured speeds can be very different. These write and read speeds are expressed in MB/s. There are several utilities available to find out the performance of your M.2 SSD. The most widely used utility is CrystalDiskMark, a free and comprehensive software to measure the write and read speed of your hard disk. Start by downloading the software and installing it. By applying CrystalDiskMark, you can set the number of passes, the size of the write and read blocks and the Mbps or Gbps scale. To start your test, choose the drive letter and therefore the speed of the disk to be evaluated. Then launch the test by closing all open programs by clicking on the All button. The tool will first perform a read test and then move to the write test.
Optimizing your M.2 SSD under Windows
You
should always leave a free space for a great longevity and performance of an SSD. Most M.2 SSDs use a wear balancing algorithm. If you fill up a drive, it can slow down. To improve performance, it's best not to format the storage space, but to leave some free space on your M.2 SSD and leave 25% of the SSD's disk space free for best performance. Never defragment an SSD. Disable the Hibernate mode of your Windows by default. To free up more space by disabling Hibernate, type the following command: powercfg -h off in a command prompt. Disable disk indexing. This is a good feature but useless on an M.2 SSD. Then finally, try adjusting the paging setting as well to balance performance and space usage.
Importance of a BIOS configuration for M.2 NVMe PCIe SSDs
When
you install a new M.2 NVMe PCIe SSD, you'll notice messages referring to a configuration to improve the speed of NVMe SSDs, or whether or not to enable shared bandwidth between the SATA and NVMe ports. Understanding the concepts behind this technical aspect, and knowing where to find detailed information will allow you to configure your hardware for optimal performance. This setting will help you avoid malfunctions, such as a hard drive or SSD that is not recognized by the system.
The best M.2 SSD depends on your needs and your budget. Read our buying guide to find out which products are the best right now.
Most of your PC's original storage is limited in capacity as a boot drive and slower for storage. Once you have the operating system and your data installed, you will quickly find that the drive is running out of space. To remedy this, you will need to clone the original M.2 SSD to a larger M.2 SSD to get more space and speed up your system.
Because of their compact size, M.2 drives do not have the ability to cool themselves and must generally rely on passive airflow. As a safety precaution, all vendors include some form of thermal limiting on their drives, which limits the flow once a certain temperature is exceeded.
Having two powerful storage devices will speed up the performance of your PC. But it's worth considering if your motherboard has another M.2 port.
To find out if your PC is compatible with an M.2 SSD, simply go to the manufacturer's website and look up the part numbers of your equipment. Or if you are able to open the shell of your PC, try to check the different connectors and slots of your laptop.
Every month we help more than 1 000 000 people buy better and smarter.
Copyright © 2022 - Made with ♥ by buyingbetter.co.uk
Your reviews and buying guides 0% advertising, 100% independent!